Injection molding is a widely-used manufacturing process that produces a wide array of products, from simple parts like bottle caps to more complex structures such as automotive components or medical devices. Let’s take a closer look at this influential manufacturing process and learn how an injection molding machine works.
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a process where molten plastic material is injected into a mold cavity, then cooled and solidified to create the final product. This method allows manufacturers to produce intricate shapes and high precision parts while minimizing waste and ensuring consistency throughout production.
Main Components of an Injection Molding Machine
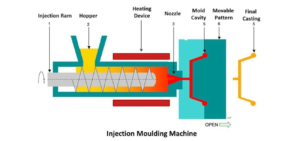
Injection Unit: The injection unit is responsible for heating and injecting the molten plastic material into the mold.
Clamping Unit: This unit clamps and holds the mold together during the injection, cooling, and ejection process.
Hydraulic System: The hydraulic system provides the force required to operate the clamping and injection components.
Control System: This system controls the parameters and operations of the injection molding process, such as temperature and pressure.
How Does an Injection Molding Machine Operate?
The functioning of an injection molding machine usually involves four significant steps:
- Melting the Plastic Material
The process begins with the granular plastic material being fed into a hopper present in the injection unit. The material is then passed through a heated barrel, where it becomes molten through a combination of heating elements and friction generated by a reciprocating screw. - Injecting the Molten Plastic
As soon as the plastic melts, the injection unit’s reciprocating screw pushes the molten material forward into the mold cavity. This is done under high pressure, ensuring that the plastic fills the entire mold cavity and takes the shape of the desired part. - Cooling and Solidifying
Once the mold cavity is completely filled, the plastic material is allowed to cool and solidify. During this stage, the clamping unit holds the mold halves securely to prevent the leakage of molten plastic. The cooling process usually involves circulating water through the mold to help dissipate heat faster. - Ejecting the Final Product
After the plastic material has cooled and solidified, the clamping unit releases the mold, and the two halves separate. Then, an ejection system pushes the newly-manufactured part out of the mold and onto a conveyor or collection bin.
Advantages of Injection Molding
High Precision: Injection molding machines can produce intricate shapes and designs with close tolerances.
Consistency: The process ensures that each part produced is consistent in quality.
Reduced Waste: Excess material from the manufacturing process can be recycled and reprocessed.
Faster Production: Due to the automated nature of the process, injection molding machines can produce a high volume of parts relatively quickly.
Conclusion
Injection molding has revolutionized the manufacturing world by enabling the production of intricately designed, high precision, and consistent parts on a large scale. Understanding the workings of an injection molding machine provides insight into this impressive process, which plays a critical role in numerous industries.